5 Reasons Why Electronic Manufacturers Should Use Etching
Leave a CommentIn today’s interconnected world, the demand for electronic devices and systems is rapidly increasing across all industry sectors. Consequently, electronic component manufacturers face the challenge of selecting the most efficient and cost-effective manufacturing processes that guarantee optimal performance. Here are five reasons why MET Manufacturing Group believes electronic manufacturers should use etching:
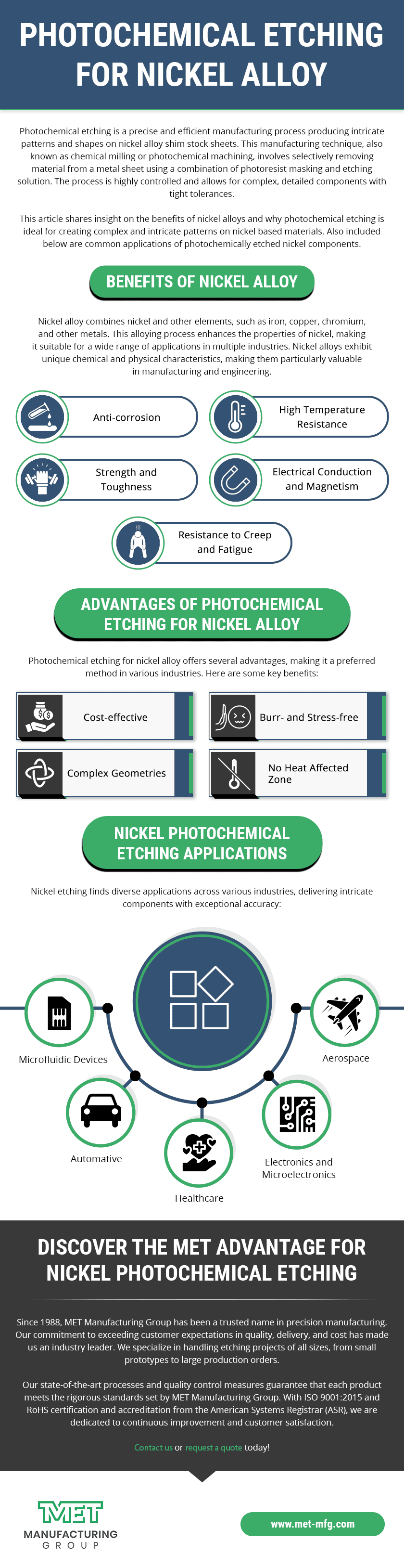
1. Material Versatility
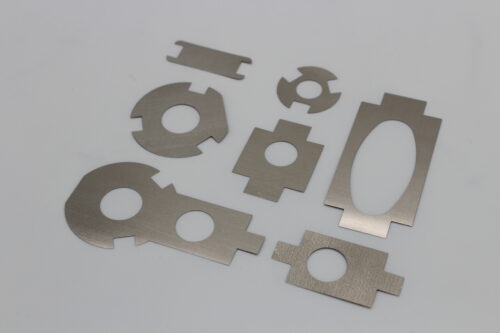
Etching is a versatile process that can work with almost any metal, making it an ideal choice for creating electrical components. Unlike traditional machining methods such as stamping and laser cutting, which may encounter challenges when dealing with hard, soft, or brittle metals, etching is not limited by the properties of the materials used.
- Copper: Known for its excellent electrical conductivity, copper is widely used in electrical components. Post-process plating can improve its corrosion resistance.
- Beryllium Copper (BeCu): This highly conductive copper alloy is durable and easy to form post-etching, making it ideal for electrical contacts.
- Brass: A copper and zinc alloy known for its high electrical and thermal conductivity, strength, and corrosion resistance. It’s ideal for contacts, connectors, and busbars.
- Phosphorous Bronze: This bronze alloy has superior spring qualities, high fatigue strength, excellent formability, and high corrosion resistance, making it great for battery contacts and springs.
- Nickel Silver: Used in EMI/RFI shielding, this copper, nickel, and zinc alloy is known for its high corrosion resistance and solderability.
- Steel: While not as conductive as other materials, tin plating can significantly enhance its conductivity and solderability. Cold-rolled steel is known for its strength and high formability.
- Stainless Steel: Highly resistant to corrosion with excellent thermal conductivity, making it popular for precision metal shims, springs, and filters.
2. Zero Thermal Stress
The high temperatures associated with traditional machining methods can cause material deformities due to thermal stress, impacting the performance of the metal component. Chemical etching eradicates the potential of parts being affected by thermal stress. The process dissolves the metal parts simultaneously rather than at localized points of contact, unlike laser cutting and wire EDM, which can introduce thermal stress along the edges.
3. Zero Burrs or Micro Burring
Traditional machining processes can leave burrs that negatively impact the performance of electrical components. For example, laser cutting can leave micro burrs on the metal’s surface, while stamping can leave partial burring. Even slight burring can cause issues such as electrical short circuits, interference interruptions, plating build-up at the component’s edges, decreased formability, inaccurate dimensional tolerances, and scratches on the surface that can affect mating components. Photochemical etching dissolves unwanted materials on a molecular level, resulting in smooth surfaces and a precision-etched profile, eliminating the need for secondary deburring operations.
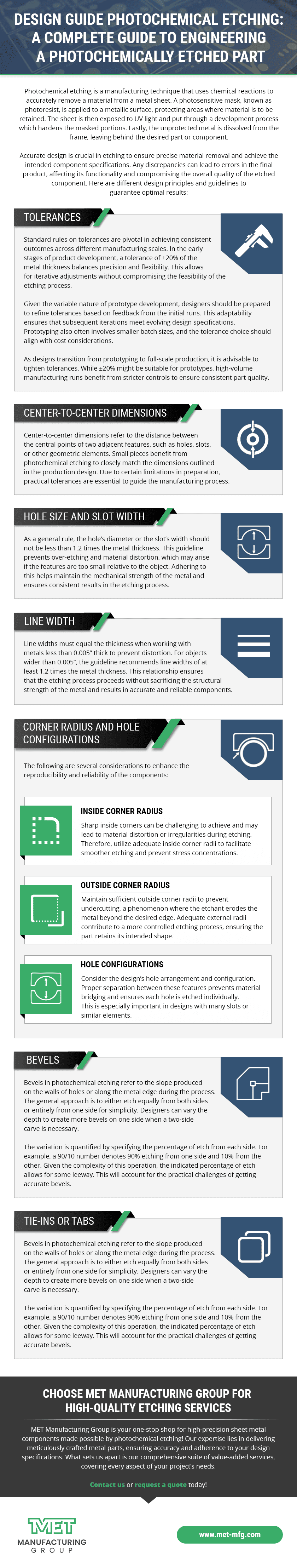
4. Suitable for Thin Materials and Complex Designs
As electronic devices become progressively smaller, there is a need for small-scale, lightweight components with complex designs. These microelectronic parts are usually machined from thinner metals and require tighter dimensional tolerances. Chemical etching is the optimum process for producing microelectronic components with complex patterns such as lead frames and filters. This process enables the simultaneous machining of features such as holes and slots, saving time and money compared to alternatives such as laser cutting, wire EDM, and stamping. Additionally, chemical etching offers the ability to partially etch a metal surface, creating fold lines valuable for components requiring forming.
5. Easy to Modify Tooling and Rapid Prototyping
The ability to test and modify designs cost-effectively is essential in the prototyping stage. Chemical etching makes it easy to revise electronic parts using low-cost digital photo-tooling. The process also allows for multiple-part designs that require the same material and thickness to be placed on the same tooling, reducing costs and lead times.
Summary
Chemical etching is a highly versatile and innovative process that electronic component manufacturers should consider for creating a wide range of electronics and microelectronic components. The process offers a variety of metal etching material capabilities, is resistant to thermal stress, remains burr-free, is suitable for thin materials and complex designs, and allows easy modification of tooling and fast prototyping. By taking advantage of these benefits, manufacturers can select the most efficient and cost-effective manufacturing processes that guarantee optimal performance.